Key Takeaways
- 5G networks use a variety of frequencies to provide more reliable coverage for devices than 4G networks.
- 5G has higher speed and latency thresholds compared to 4G, providing faster download speeds.
- 5G is more energy-efficient than 4G and has the capability to support connectivity for far more devices on one network.
When 4G data was announced, it was revolutionary. Now, 5G is touted as being superior in every way. Despite all the praise, articles usually aren’t upfront about what actually makes 5G even better than 4G LTE. As it turns out, there are actually many advantages, especially for the individual users.
5G Network Architecture Offers Better Coverage For More Devices
To explain how 5G networks are superior to 4G, I’ll have to talk about some technical things. But don’t worry, I’ll keep it pretty simple. Let’s start with bandwidth. Bandwidth is the capacity of a network. The more bandwidth a network has, the more devices it can support. When one device on a network is using up a lot of data, it impacts the ability of all other devices on the network to send and receive data.
These days, more and more devices are connected to a single network in modern homes. Laptops, phones, smart TVs, lights, and even some appliances connect to a single network. That means a lot of devices are sharing bandwidth, and simply out, 4G networks don’t have as much bandwidth to share as 5G networks do. That’s because 5G networks are designed to carry information across multiple bands, with each excelling in different areas.
These are known as low-band, mid-band, and high-band frequencies. High-band frequencies, also called mmWave, are capable of carrying a lot of data even in dense areas, so a lot more devices can be connected to one network without impacting data upload and download speeds.
However high-band frequencies are vulnerable to blocking by physical barriers like buildings and walls. To combat this, 5G uses mid-band frequencies, which aren’t quite as fast as high-band frequencies but don’t have as many issues with blocking. Finally, low-band frequencies allow 5G to carry data over incredibly long distances.
By relying on all three bands, each with its own strengths, 5G offers better coverage to more devices in more situations than 4G is capable of. It has the means to offer good coverage in densely populated urban environments, but it can also reach out to distant rural areas more effectively as well. Overall, its coverage is far more robust and reliable in nearly every situation.
5G Has Much Higher Speed and Latency Thresholds
Alongside bandwidth, there are two other important aspects of networks to talk about: speed and latency. Bandwidth is the highest theoretical rate at which your network can download data, but speed is the actual rate at which things download. Think of it like a car speedometer. The top theoretical speed of your car is the network bandwidth, but the speed your car can practically reach is the network speed.
Latency, on the other hand, is how long it takes your network to upload and download data. All that really matters is that 5G has much better performance in all of these areas than 4G does, and that’s good for your online experience. For example, 4G LTE speed tops out at around 100Mbps. 5G has the potential to be around ten times faster than this, though many factors impact the actual speed.
This means everything you do on a 5G network is much faster than it is on a 4G network, whether that’s streaming a movie, loading a webpage, downloading a video game, or anything else. 5G may not always hit that theoretical ten times greater speed than 4G, but the fact remains that it has a much higher speed and latency threshold that 4G networks couldn’t match even on their best days.
5G is More Energy Efficient than 4G
This one might come as a surprise to some, but if you care about being as eco-friendly as possible in your life, 5G networks fit the bill. Not that we as consumers get to choose which networks are being used around the world, but as society inevitably moves towards phasing out 4G networks, our energy efficiency will benefit from 5G dominance.
With the amount of energy it would take a 4G network to download three hundred movies, a 5G network could download five thousand movies. That’s over a dozen times more efficient. Now this might not seem like such a big deal, but this increased energy efficiency will make a big impact in the future.
Just imagine all of the things people do on networks already. How many movies and songs are streamed, how many video game matches and patches there are, and how many minutes are spent on the internet, uploading and downloading data. There are hundreds of millions of people using networks to do these things every single hour of every day.
On an individual level, you might not notice the impact. Still, when we consider how much energy is used by networks every day, it’s clear that the massive efficiency advantage offered by 5G over 4G will be hugely beneficial for both the environment and energy production.
5G Will Offer Possibilities 4G is Incapable of Supporting
As far as the individual consumer is concerned, the main appeal of 5G over 4G networks is that 5G will give you faster speeds on a more consistent basis, at least for now. Its impact on your life might grow even more noticeable in the coming years. The advanced capability of 5G networks provides an opportunity for some interesting opportunities.
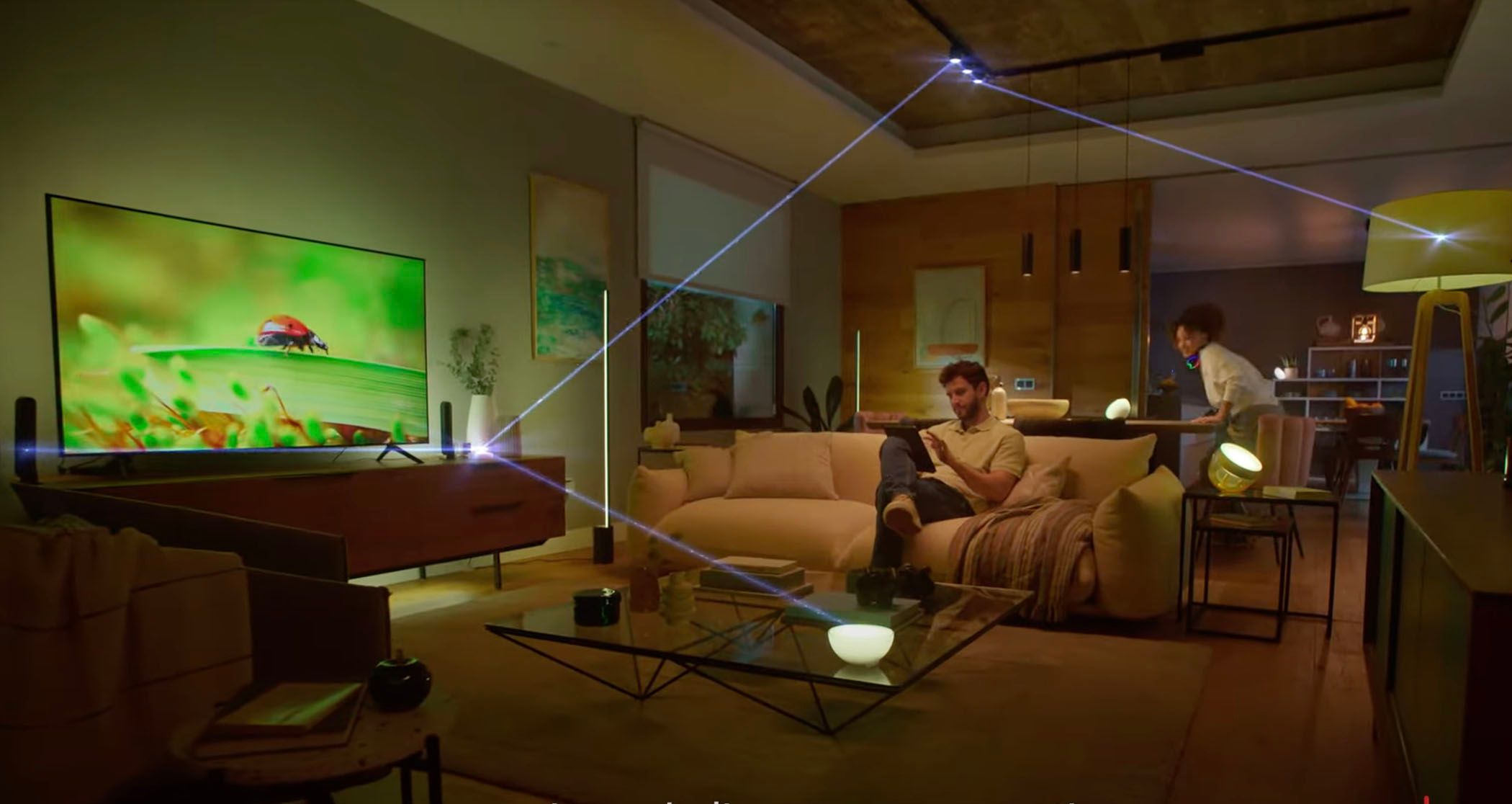
For example, both homes and cities are likely to become more connected than ever in the future. Instead of individual smart devices, 5G could support the concept of entire smart homes, much like those futuristic utopian houses you often see in science fiction. Even today, some cities are already utilizing 5G networks to connect things like traffic monitoring, air and water quality control, and management systems.
One day in the not-so-distant future, we may be graced with a greater level of inter-connectivity than 4G networks could ever provide. For now though, the main benefit of 5G networks is still just that your phone can do everything faster than it could have on a 4G network.
Admittedly, there are other technical differences between 4G and 5G networks: there are pages and pages of information about it that most of us (including me) probably wouldn’t be able to understand. Ultimately, all you really need to know is that 5G really is several magnitudes better than 4G in terms of speed and performance, and it is, without a doubt, the way of the future.